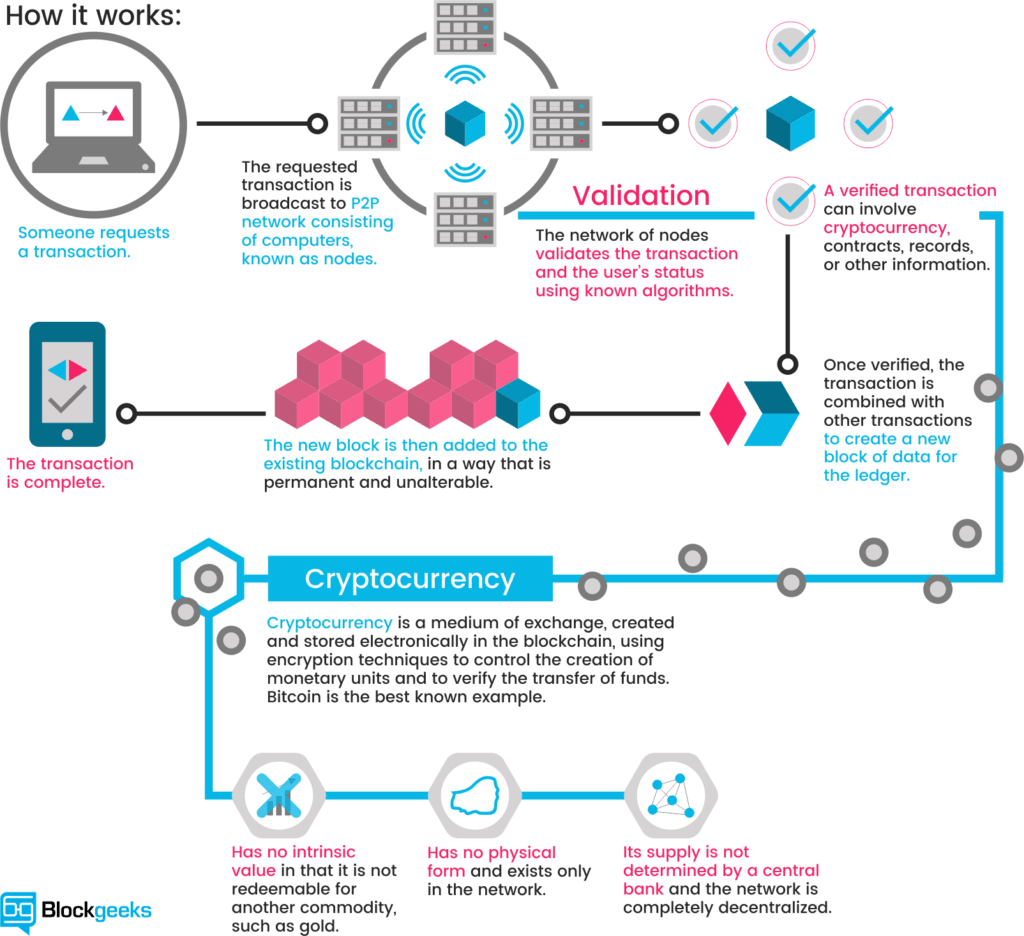
Crypto vendor meaning takes center stage in the ever-evolving cryptocurrency landscape, offering insights into the key players that facilitate digital currency transactions. As the crypto world expands, understanding who these vendors are and their importance becomes essential for anyone navigating this space.
From exchanges that allow users to buy and sell cryptocurrencies to wallets ensuring secure storage, crypto vendors play a pivotal role in the ecosystem. This overview explores the various types of vendors, their functions, and how they contribute to the growth and adoption of digital currencies.
Understanding Crypto Vendors
The rise of cryptocurrencies has led to the emergence of various players in the market, one of which is the crypto vendor. A crypto vendor is a business that provides services related to the buying, selling, or trading of cryptocurrencies. These vendors play a crucial role in the cryptocurrency ecosystem by facilitating transactions and ensuring that users can easily access digital currencies.
By understanding what a crypto vendor is, we can appreciate their significance in the evolving landscape of digital finance.Crypto vendors come in many forms, including exchanges, wallets, and payment processors. Each type serves a unique purpose in the cryptocurrency marketplace. For example, exchanges allow users to trade different cryptocurrencies, while wallets provide a secure way to store them. Payment processors help businesses accept cryptocurrencies as a mode of payment.
Together, these vendors create an infrastructure that supports the use and adoption of cryptocurrencies.
Types of Crypto Vendors
Crypto vendors can be categorized into several types, each offering unique functionalities that cater to different user needs in the cryptocurrency market. The primary types of crypto vendors include:
- Exchanges: These platforms enable users to buy, sell, and trade cryptocurrencies. They often provide features such as market analysis, price charts, and trading tools.
- Wallets: Digital wallets store cryptocurrencies securely. They can be hot wallets (connected to the internet) or cold wallets (offline storage) and come with varying levels of security to protect user assets.
- Payment Processors: These vendors facilitate cryptocurrency transactions for businesses, helping them accept digital currencies as payment for goods and services.
To provide a clearer overview, here’s a comparison table highlighting the features of different types of crypto vendors:
| Type of Vendor | Primary Functionality | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Exchange | Trading cryptocurrencies | Coinbase, Binance |
| Wallet | Storing cryptocurrencies | Exodus, Ledger |
| Payment Processor | Facilitating transactions | BitPay, CoinGate |
Importance of Crypto Vendors
Crypto vendors are vital in promoting the adoption of cryptocurrencies across various demographics. They provide the necessary tools and platforms for users to engage with digital currencies, thereby increasing overall market participation. By facilitating transactions and simplifying the buying process, they contribute to greater accessibility and usability of cryptocurrencies.Moreover, crypto vendors play a significant role in enhancing security measures within the industry.
With the rise in cyber threats and fraud, reputable vendors implement robust security protocols to protect user assets and sensitive information. This includes two-factor authentication, encryption, and regular security audits.In addition to security, compliance with regulations is essential for crypto vendors. They must adhere to local laws and guidelines to ensure that their operations are lawful. This compliance not only builds trust with users but also helps in legitimizing the cryptocurrency space as a whole.
Services Offered by Crypto Vendors
Crypto vendors provide a wide range of services to cater to the diverse needs of users. Common services include:
- Buying cryptocurrencies with fiat currency
- Selling cryptocurrencies for fiat or other digital currencies
- Trading cryptocurrencies on various markets
Additionally, many vendors offer supplementary services that enhance user experience, such as:
| Service | Description |
|---|---|
| Staking | Users can earn rewards by locking their cryptocurrencies in a wallet to support network operations. |
| Lending | Platforms allow users to lend their cryptocurrencies to earn interest. |
| Rewards Programs | Some vendors offer incentives for trading or holding certain cryptocurrencies. |
These services not only increase user engagement but also help in fostering a more vibrant cryptocurrency community.
Risks Associated with Crypto Vendors
While crypto vendors provide essential services, users should be aware of potential risks associated with their operations. These risks may include:
- Security vulnerabilities leading to loss of funds
- Regulatory changes impacting service availability
- Market volatility affecting trading outcomes
To mitigate these risks, reputable crypto vendors should implement comprehensive security measures such as:
“Utilizing multi-signature wallets, regular security audits, and real-time fraud detection systems are crucial in safeguarding user assets.”
Users can also adopt best practices such as enabling two-factor authentication, using cold wallets for long-term storage, and staying informed about market trends to enhance their protection against potential threats.
Future Trends in Crypto Vendors
The landscape of crypto vendors is continually evolving, and several trends are emerging that may shape their future operations over the next five years. Noteworthy predictions include:
- Increased integration of artificial intelligence for fraud detection and user support.
- Expansion of decentralized finance (DeFi) services provided by traditional crypto vendors.
- Enhanced regulatory frameworks guiding the operations of crypto businesses.
Technological advancements such as blockchain scalability solutions and improved user interfaces are also expected to influence the way crypto vendors operate, making transactions faster and more user-friendly.As the cryptocurrency ecosystem matures, these emerging trends could significantly reshape the role and functionalities of crypto vendors, paving the way for a more robust and secure digital finance environment.
Epilogue
In summary, crypto vendors are integral to the cryptocurrency ecosystem, not only providing essential services but also driving innovation and regulatory compliance. As the market continues to evolve, staying informed about the role of these vendors will empower users to navigate the crypto space more effectively and confidently.
Query Resolution
What is a crypto vendor?
A crypto vendor refers to any service provider that facilitates transactions involving cryptocurrencies, such as exchanges, wallets, and payment processors.
How do crypto vendors enhance security?
Reputable crypto vendors implement advanced security measures such as two-factor authentication, encryption, and cold storage to protect user assets.
Are all crypto vendors regulated?
No, not all crypto vendors are regulated, but many comply with local laws to ensure trust and security for their users.
What services do crypto vendors typically offer?
Common services include buying, selling, trading cryptocurrencies, as well as staking, lending, and rewards programs.
What risks are associated with using crypto vendors?
Risks can include hacking, fraud, and regulatory changes, which users should be aware of when engaging with crypto vendors.